2224 - 滑动窗口
给定一个长度为n(n<=10^6)的数组。有一个大小为k的滑动窗口从数组的最左端移动到最右端。你可以看到窗口中的k个数字。窗口每次向右滑动一个数字的距离。
下面是一个例子:
数组是 [1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7], k = 3。
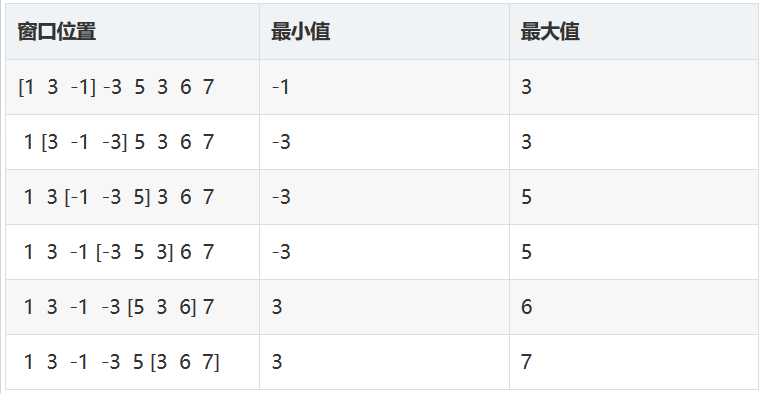
你的任务是得到滑动窗口在每个位置时的最大值和最小值。
输入
输入包括两行。
第一行包括n和k,分别表示数组的长度和窗口的大小。(k<n)
第二行包括n个数字。
输出
输出包括两行。
第一行包括窗口从左至右移动的每个位置的最小值。
第二行包括窗口从左至右移动的每个位置的最大值。
样例
输入
8 3 1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7
输出
-1 -3 -3 -3 3 3 3 3 5 5 6 7
提示
//赵锐
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct cis
{
int x;
int c;
}t;
int n, k;
vector <int> s1;
vector <int> s2;
vector <int>::iterator it;
deque <cis> maxd, mind;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
for( int i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
{
cin >> t.x;
t.c = i;
while( !maxd.empty() and maxd.back().x <= t.x )
maxd.pop_back();
maxd.push_back(t);
while( !mind.empty() and mind.back().x >= t.x )
mind.pop_back();
mind.push_back(t);
if( i >= k )
{
while( mind.back().c - mind.front().c >= k )
mind.pop_front();
s1.push_back(mind.front().x);
while( maxd.back().c - maxd.front().c >= k )
maxd.pop_front();
s2.push_back(maxd.front().x);
}
}
for( it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++ )
cout << *it << " ";
cout <<endl;
for( it = s2.begin(); it != s2.end(); it++ )
cout << *it << " ";
return 0;
}
//招力楷
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int sum;
int num;
} t;
int main(){
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
deque <node> mind(n);
deque <node> maxd(n);
vector <int> v;
vector <int>:: iterator it;
int h, i, j = 0;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> t.sum;
t.num = i;
while(!maxd.empty() and maxd.back().sum <= t.sum){
maxd.pop_back();
}
maxd.push_back(t);
while(!mind.empty() and mind.back().sum >= t.sum){
mind.pop_back();
}
mind.push_back(t);
if(i >= k){
while(mind.back().num - mind.front().num >= k){
mind.pop_front();
}
cout << mind.front().sum << " ";
while(maxd.back().num - maxd.front().num >= k){
maxd.pop_front();
}
v.push_back(maxd.front().sum);
}
}
cout << endl;
for(it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){
cout << *it << " ";
}
return 0;
}
//张皓宇
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int x , index;
}t;
int main(){
int n, k;
deque<node> maxd,mind;
vector<int>v;
vector<int>::iterator it;
cin >> n >> k;
int i, j;
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++){
cin >> t.x;
t.index = i;
while(!maxd.empty() && maxd.back().x <= t.x)
maxd.pop_back();
maxd.push_back(t);
while(!mind.empty() && mind.back().x >= t.x)
mind.pop_back();
mind.push_back(t);
if(i >= k){
while(mind.back().index - mind.front().index >= k)
mind.pop_front();
cout << mind.front().x << " ";
while(maxd.back().index - maxd.front().index >= k)
maxd.pop_front();
v.push_back(maxd.front().x);
}
}
cout << endl;
for(it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++){
cout << *it <<" ";
}
return 0;
}
//韩志尚
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int x,y;}t;
int main(){
deque<Node> maxd,mind;
vector<int> v;
vector<int>::iterator it;
int i,j,n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>t.x;
t.y=i;
while(!maxd.empty()&&maxd.back().x<=t.x)
maxd.pop_back();
maxd.push_back(t);
while(!mind.empty()&&mind.back().x>=t.x)
mind.pop_back();
mind.push_back(t);
if(i>=k){
while(mind.back().y-mind.front().y>=k)
mind.pop_front();
cout<<mind.front().x<<" ";
while(maxd.back().y-maxd.front().y>=k)
maxd.pop_front();
v.push_back(maxd.front().x);}}
cout<<endl;
for(it=v.begin();it!=v.end();it++)
cout<<*it<<" ";
return 0;}
来源
vector 单调队列